Press releases
Emulsion microdroplets can swim by producing their own flagella
2021-07-15
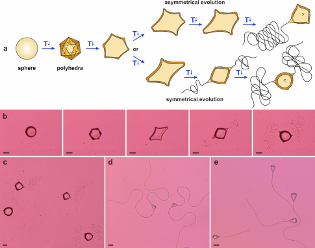
Researchers from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw, University of Cambridge, Queen Mary University of London and University of Sofia have shown that slow cooling of a suspension of oil droplets with surfactant in water may lead to non-spherical shapes of the droplets, which can produce filamentous structures resembling bacterial flagella. The filaments induce motion of the droplets, and the process is fully reversible via cyclic changes of the temperature of their environment. An article describing the findings has just been published in “Nature Physics”. | More
Lasing in biological materials as a structure-sensitive research tool
2021-06-22
A team of scientists from the Ultrafast Processes Laboratory at the Faculty of Physics of the University of Warsaw, supported by a researcher from the Chalmers University of Technology (Sweden), showed how to detect changes in the DNA structure using all-optical methods based on the emission of light. This was achieved by time-resolved measurements of the intensity of light emitted by an organic dye bound to the studied material after it was excited by a short pulse of laser light and by using the phenomenon of light amplification in a medium excited by a strong laser pulse. A paper describing these experiments found its way to the cover of one of the leading magazines in the field of physical chemistry, The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. | More
How is angular momentum generated in nuclear fission?
2021-02-25
A series of measurements performed at the Laboratory of the Physics of the two infinities Irène Joliot-Curie (IJCLab) in France resulted in a key observation that allows to explore the mechanism of angular momentum generation in nuclear fission. Analysis of the properties of radiation emitted in the fission reactions of the 238U, 232Th, and 252Cf atomic nuclei revealed no correlation between the angular momenta of the resulting fission fragments. This latest finding implies that, contrary to the predictions of most fission models, the sources of angular momenta are separate, and it must be generated after the nucleus splits. The results, published in the Nature journal, are the effect of collaboration between physicists from the international Nu-ball research group, including researchers from the Faculty of Physics of the University of Warsaw. | More
Second order optical merons, or light pretending to be a ferromagnet
2021-02-22
The scientists have demonstrated how to structure light such that its polarization behaves like a collective of spins in a ferromagnet forming half-skyrmion (also known as merons). To achieve this the light was trapped in a thin liquid crystal layer between two nearly perfect mirrors. Skyrmions in general are found, e.g., as elementary excitations of magnetization in a two-dimensional ferromagnet but do not naturally appear in electromagnetic (light) fields. | More
An Earth-sized rogue planet discovered in the Milky Way
2020-10-29
Over four thousand extrasolar planets have been discovered to date. Although many of the known exoplanets do not resemble those in our solar system, they have one thing in common – they all orbit a star. However, theories of planet formation and evolution predict the existence of free-floating (rogue) planets, gravitationally unattached to any star. Indeed, a few years ago Polish astronomers from the OGLE team from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw provided the first evidence for the existence of such planets in the Milky Way. Writing in Astrophysical Journal Letters, OGLE astronomers announced the discovery of the smallest rogue planet found to date. | More
Microscopy beyond the resolution limit
2020-10-07
The Polish-Israeli team from the Faculty of Physics of the University of Warsaw and the Weizmann Institute of Science has made another significant achievement in fluorescent microscopy. In the pages of the Optica journal the team presented a new method of microscopy which, in theory, has no resolution limit. In practice, the team managed to demonstrate a fourfold improvement over the diffraction limit. | More
Dr. Przemysław Mróz awarded the Frank Wilczek Award of the Jagiellonian University and the Kościuszko Foundation
2020-07-17
Dr. Przemysław Mróz has been announced the first laureate of the new Frank Wilczek Award. The prize was established to recognize outstanding young researchers who have made a significant contribution to physics, astronomy or closely related areas. The award patron – Professor Frank Wilczek, physicist from the Massachusets Insitute of Technology – is the laureate of the 2004 Nobel Prize in Physics . The Award is funded by the Jagiellonian University and the Kościuszko Foundation. Dr. Przemysław Mróz has been awarded for the scientific achievement entitled: Free-floating planets – a new category of exoplanets. | More
The smallest micro-gripper, grown on optical fibers, is operated remotely with light
2020-07-15
Researchers at the Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw, used the liquid crystal elastomer technology to demonstrate a series of micro-tools grown on optical fibers. The 200-micrometer gripers are controlled remotely, without electric wiring or pneumatic tubing, with green light delivered through the fibers – absorbed light energy is directly converted into the gripper jaws' action. | More
Dr. Przemysław Mróz awarded the International Astronomical Union 2019 PhD prize
2020-06-10
Dr. Przemysław Mróz has been awarded the International Astronomical Union PhD prize for outstanding scientific achievements of astronomy PhD students around the world for his dissertation Astrophysical applications of gravitational microlensing in the Milky Way. The thesis was written under the supervision of Professor Andrzej Udalski from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw. | More
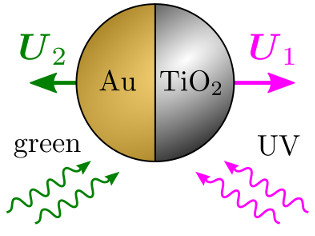
Active particles with light-switchable propulsion direction and reversible interactions
2020-06-03
Researchers from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw, ETH in Zurich and the University of Cambridge have synthesized and analysed active microparticles self-propelling in a fluid and reversing their propulsion direction depending on the wavelength of illuminating light. A research article summarising their work has recently been published in Nature Communications. | More