Press releases
Science in the kitchen
2023-06-22
Take four brilliant physicists who specialize in fluid mechanics and put them in the kitchen. Give them pots, pans, basic foodstuffs, and a bottle of champagne. Add a COVID-19 pandemic, a pinch of boredom, and a handful of good ideas. Stir, wait, and voilà - you have a "delicious" publication that will teach you how bubbles are created in champagne, how to brew the perfect espresso, and how "kitchen revolutions" can contribute to innovations in many fields, including biomedicine and nanotechnology. | More
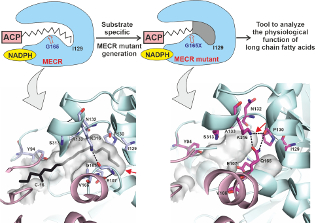
Researchers confirmed the role of long-chain fatty acids in cellular respiration
2023-06-02
Cellular respiration is a complex and highly regulated process that allows cells to draw energy from nutrition. An international team of scientists from Finland, Germany and Poland have investigated the important role of long-chain fatty acids in guiding this process. The findings, published in Nature Communications, will shed light on the understanding of mitochondrial function that involve disruptions in cellular energy metabolism. | More
Researchers at the Faculty of Physics of the University of Warsaw have created a new, highly efficient converter of quantum information carriers
2023-05-25
Researchers at the University of Warsaw's Faculty of Physics have developed a new, highly efficient technique that makes quantum information transmission dozens of times faster. The results of the research, published in the prestigious journal Nature Photonics, may in the near future contribute to the development of superfast quantum Internet connections. | More
Defying gravity
2023-04-17
Physicists from the University of Utrecht and the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw have observed - for the first time experimentally - the Brazil nut effect in a mixture of charged colloidal particles. Until now, it was thought that an influx of external energy was required to create this effect - but the researchers were able to confirm that the process can occur spontaneously. The findings, published in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), could find applications in a wide range of fields, from geology to soft matter physics. | More
Three time dimensions, one space dimension
2022-12-23
How would our world be viewed by observers moving faster than light in a vacuum? Such a picture would be clearly different from what we encounter every day. We should expect to see not only phenomena that happen spontaneously, without a deterministic cause, but also particles traveling simultaneously along multiple paths - argue theorists from universities in Warsaw and Oxford. Also the very concept of time would be completely transformed — a superluminal world would have to be characterized with three time dimensions and one spatial dimension and it would have to be described in the familiar language of field theory. It turns out that the presence of such superluminal observers does not lead to anything logically inconsistent, moreover, it is quite possible that superluminal objects really exist. | More
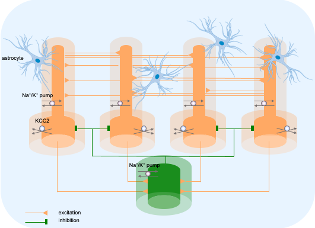
Changes in ion concentrations responsible for seizures
2022-12-22
An epileptic seizure may begin with firing of inhibitory neurons in the brain and changes in ion concentrations in the environment around the neurons. This mechanism, observed experimentally in an animal model of the guinea pig brain, was confirmed in a computer model of nerve cells, created at the Faculty of Physics of the University of Warsaw. The results of research conducted by a group of Polish and Italian scientists, published in the eLife journal, may contribute to the development of new antiepileptic therapies. | More
An artificial polariton neuron as a step towards photonic system that mimics the operation of the human brain
2022-10-24
Scientists from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw and the Polish Academy of Sciences used photons to create a spiking neuron, i.e. the basic element of the future photonic neural network processor. The so-called neuromorphic devices, i.e. systems that imitate the behaviour of the biological brain, which researchers are working on, are the future of artificial intelligence, as they allow for much faster and more effective information processing. We can read about the results of their work in the latest "Laser and Photonics Review”. | More
The annihilation of exceptional points from various degeneration points was observed for the first time in the world
2022-10-14
A team of researchers from the University of Warsaw in Poland, the Institute Pascal CNRS in France, the Military University of Technology in Poland and the British University of Southampton has shown that it is possible to control the so-called exceptional points. For the first time, physicists also observed the annihilation of exceptional points from different degeneracy points. You can read about the discovery that may contribute to the creation of modern optical devices in the latest “Nature Communications”. | More
Physicists from the University of Warsaw and the Military University of Technology have developed a new photonic system with electrically tuned topological features
2022-10-14
Scientists from the Faculty of Physics of the University of Warsaw in cooperation with the Military University of Technology, the Italian CNR Nanotec, the British University of Southampton and the University of Iceland obtained a new photonic system with electrically tuned topological features, constructed of perovskites and liquid crystals. You can read about the discovery, that can be used in the creation of efficient and unconventional light sources, in the latest "Science Advances". | More
Astronomers find a “cataclysmic” pair of stars with the shortest orbit yet
2022-10-11
The stars circle each other every 51 minutes, confirming a decades-old prediction. An international team of astronomers, with the participation of dr Przemysław Mróz from the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Warsaw, have now discovered a stellar binary, or pair of stars, with an extremely short orbit, appearing to circle each other every 51 minutes. The system seems to be one of a rare class of binaries known as a “cataclysmic variable,” in which a star similar to our sun orbits tightly around a white dwarf — a hot, dense core of a burned-out star. | More